Businesses are no longer limited to local boundaries and the expansion of customer base increases the workforce. With continuous development of business tasks, the management of the workforce requires the information to reach every employee whenever needed.
The proper management and security of information are propagated by the faded term Mobile Device Management (MDM) and Mobile App Management (MAM), which eventually became part of Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM).
Mobile management services have become an integral part of the business conduct for the flow of crucial information across the organization and therefore, there is a huge demand to hire app developers.
To decide the ideal enterprise mobility solution, you need to go dig into the roots of EMM and weigh them as per respective business use cases:
What is Enterprise Mobility Management?
Enterprise mobility solution offers employees the ability to reach data over the company's network. EMM is a top end solution with the combined ability of MDM and MAM for additional management features, like threat mitigation and security.
EMM is not just about incorporating the advancement, but also about separating personal data from device data. It allows administrators to reach out to the employees with mobile devices for being more productive.
Mobile application development companies are facing high demand for these solutions. EMM has come out of MDM that deals in device level transaction.
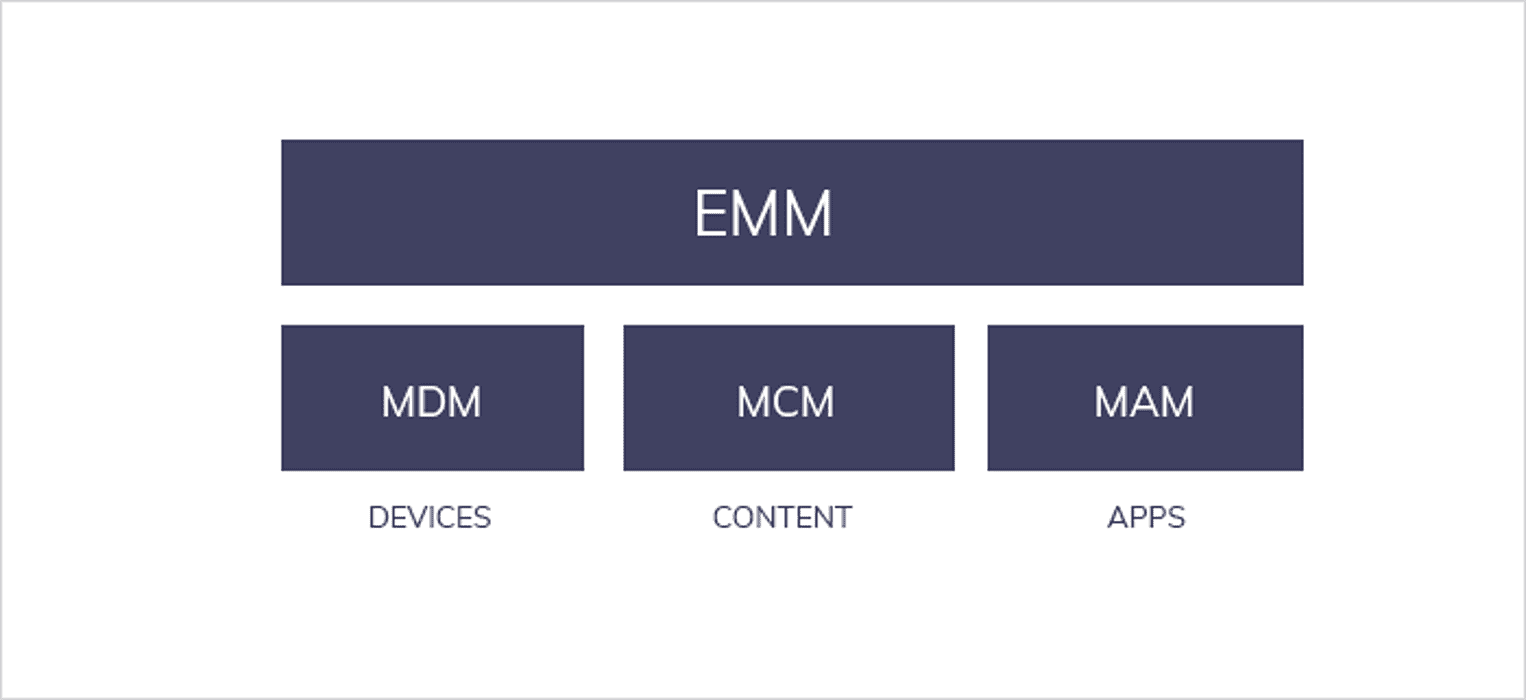
EMM provides the user with the following features:
- Secure access to all apps and data on the network.
- Security from malware and other data loss.
- High level of mobility control.
Evolution of EMM:
EMM involves the blend of MDM, MAM, and MCM along with identity management tool. These technologies are usually included in a larger platform or EMM software suites that make the game too large for small companies.
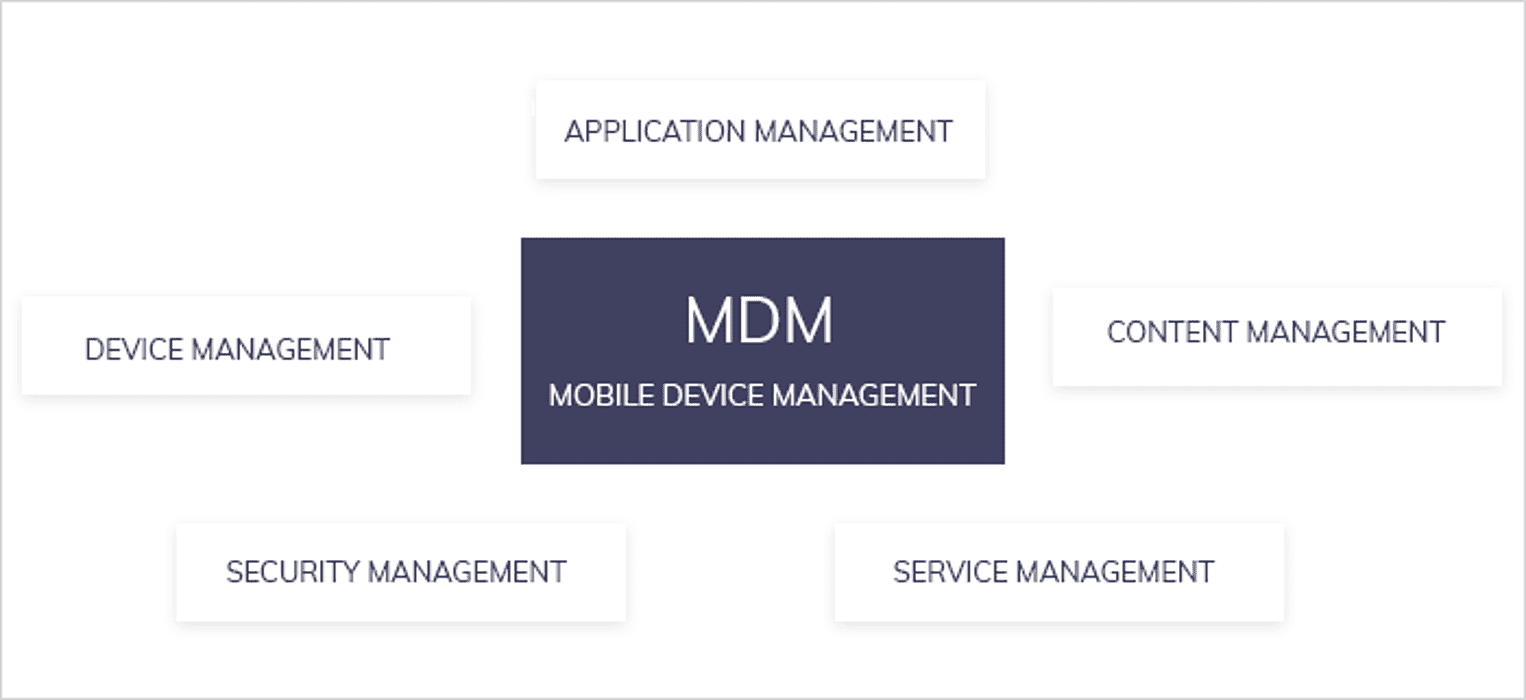
What is Mobility Device Management?
Mobility device management gives users access to information over the company's network. It depends on the endpoint mobile device and central hub or server for transacting the information.
In data centers, the administrator uses the management console interface to configure settings by setting up the API in mobile OS (partner with a renowned android app development company for configuration of API).
MAM: MAM works at the granular level that allows the admin to set policies and rules for a particular app or set of apps. MAM is integrated with both the operating system and device, where few apps have specific MAM APIs while other apps stay dependent over built-in device level tools.
MCM: MCM is used for approving an application to transact corporate data within the organization.
Identity tools and role-based access management tools control the usage of corporate data by employees, while also enabling features that are user-friendly too.
All the above technologies address the specific issues and there is a very thin overlapping in between, which enables the productizing of EMM with the blend of MAM and MCM features to MDM.
The self-service portals and the enterprise app stores are the best examples of evolved MDM software. Let's look at how EMM and MDM are related and differ from each other and find out which is an essential factor for a mobile application development company amidst high demand.
Similarities Between EMM and MDM
By now, we have substantially done ground-level research on Enterprise Mobility Solutions, which introduces us to the hidden MDM roots. It is recommended to look at the gray areas, where they pose similarities.
Though it is clear that EMM has an advantage over MDM, and can be classed as evolved MDM, still, for potential buyers, both fulfill the same objectives of managing the user-owned or company-issued mobile devices.
After the enrollment of devices over the platforms, administrators solve the problems, push files, applications, software upgrades, wipe data, and lock devices all through the central data. The old MDM solutions were limited support for the operating system, whereas the advanced OS updates are made to support thousands of brands/models.
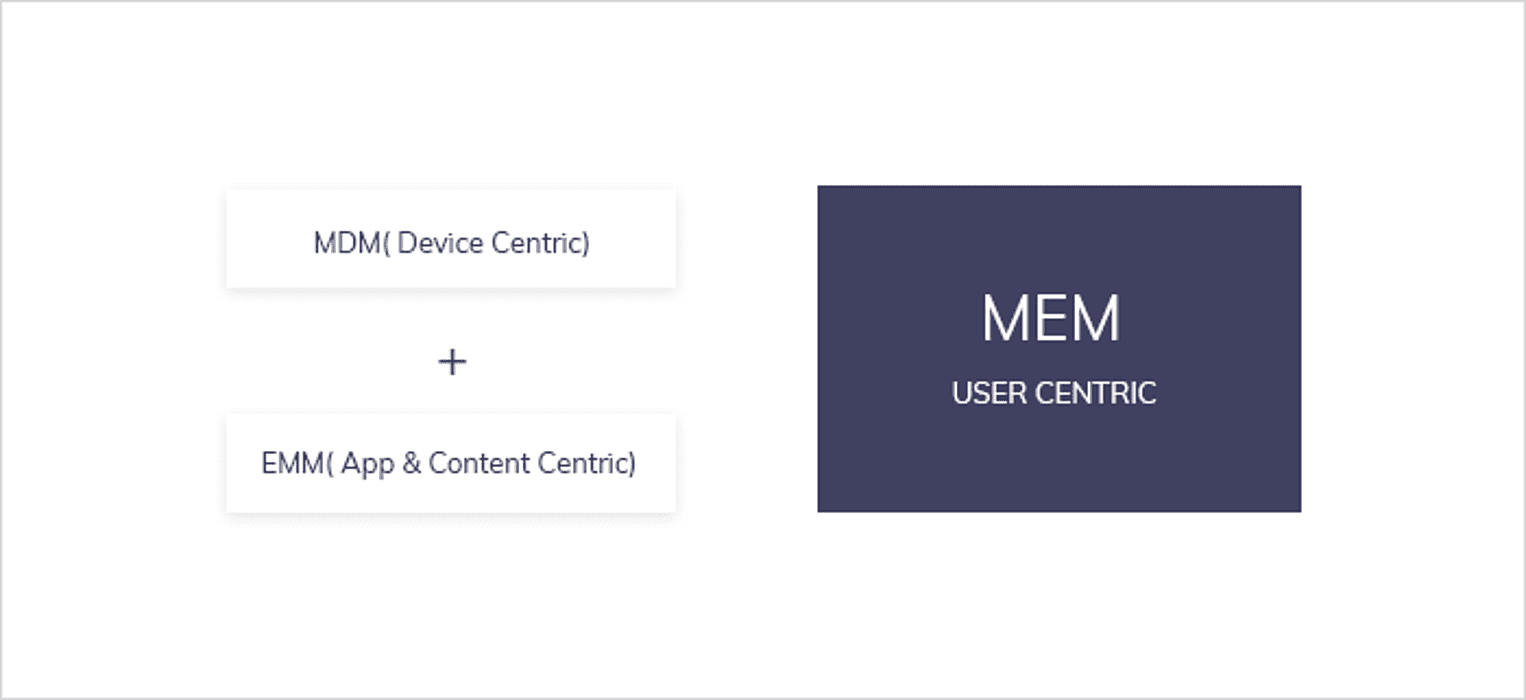
Common Functions of EMM and MDM
Any device management platform must have some specific standard functions, regardless of whether it is EMM or MDM. Similar functions of EMM and MDM are:
1. Device Inventory management: It specifically comprises the enrollment of devices and decommissioning of devices along with asset tracking. The inventory management function includes:
- Asset detail at the central hub and changelog.
- Deletion, wiping, and restoration of data from remote locations.
- User self-enrollment.
2. Use policy management: EMM and MDM platforms enable policy management along with the compliance check enforcing the required actions.
3. Security management of mobile devices: The crucial reason for the evolution of MDM is the fear of data breach. The critical function of device security is applied for protecting the integrity of data being transmitted and stored, which includes:
- Password management;
- Email security;
- Data encryption;
- Device blacklisting in critical cases;
- Detection of jailbreak.
4. Activity Monitoring: The company's device inventory is kept transparent and provides real-time visibility. With the help of MDM and EMM platforms, the IT team can keep track of the location of mobile devices and their activities. Rich dashboards offer the ability to share reports in different delivery formats to stakeholders.
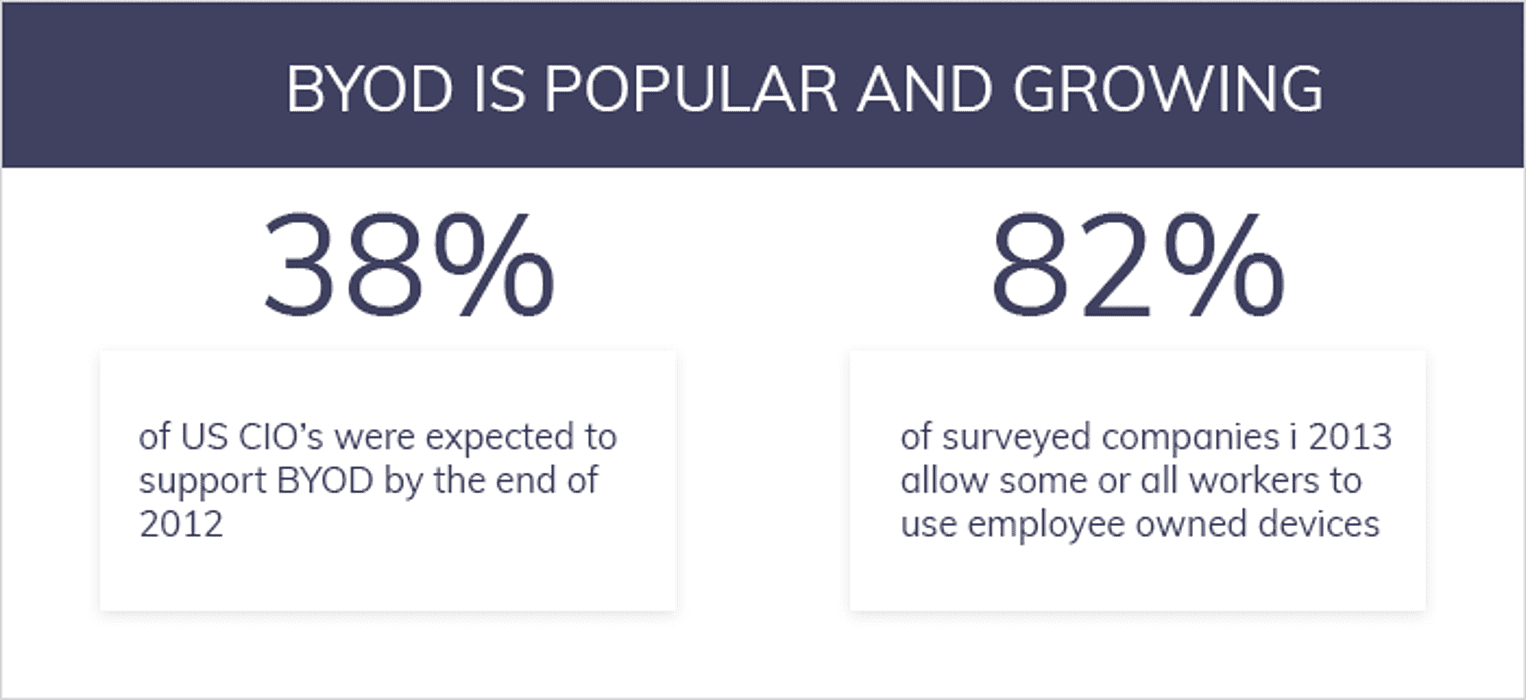
How BYOD Brought EMM Forward?
Organizations give the whole responsibility to employees to manage data through their respective devices. This is how Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) comes into play.
Mobile device management was used for long to counterbalance the security threat posed by the influx of new devices. MDM operates at device level and the data used personally and professionally can be managed from a remote location. Gradually, the organization understood that MDM is not a solution and moved to the new management system called Android EMM.
Through the year, businesses started to understand the critical shift in market and the need to manage information on employees’ devices more than strengthening the device security. Here, Enterprise Mobility Management came to the rescue for Android app development companies.
Why did the market shift to EMM?
Unlike MDM, EMM expanded the capabilities of IT to set up the usage policies of the app. The term EMM comprises:
1. Mobile Application Management: MAM refers to the configuration of the app for limiting the access of information from both the network and apps. App configuration is like putting a wrapper around an app.
2. Mobile Identity Management: The security of information depends on how it is configured to be used. The MIM not only limits the role-based access to the information but also geo-based access, thus allowing to check where the information is being used.
3. Mobile Content Management: Limiting the business content access is achieved by MCM, which also includes copy and paste restriction and restricted access to repositories.
These three mechanisms expand the power of managing mobility and provide technical capabilities for the sake of securing data and offering a pleasant user experience for administrators and employees alike.
How to Choose Between EMM and MDM?
Having an enterprise mobility solution for the business is necessary to get the best outcome for your mobile workforce and manage the workload. The EMM solution is apt for businesses, as it satisfies the criteria and leaves enough opportunity and space for the expansion with scalability. Also, it leaves no stone unturned to secure a variety of devices and integrate them with the best solution, while supporting the existing system to keep it intact.
At the core, all EMM should manage mobile devices, applications (blacklisting the app, which consumes high data), authentication, and content for the sake of security, timely availability, and authentication based control.
While choosing among the options, it is imperative to enumerate the features, which perfectly fit into the specific business needs, alongside treading parallelly to the meteoric rate of change in mobile technology, which a renowned Android app development company must be able to cope with. The cardinal rule of mobile management ensures that your IT team is able to manage all mobile devices the employees use.